Why are Hair Follicles Blocked and How Can You Reopen It?

When it comes to skin health, we often hear about common issues like acne, rashes, and dry skin. However, there’s another less-discussed yet equally important concern that can affect our skin and hair health: blocked hair follicles. Blocked hair follicles can lead to a variety of problems, including painful cysts, acne, and even hair loss. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of blocked hair follicles, exploring the causes, symptoms, prevention, and treatment options for this often-overlooked issue.
Anatomy of Hair Follicles
Before we delve into the intricacies of blocked hair follicles, it’s essential to understand the basics of hair follicles and their role in maintaining healthy skin and hair. Hair follicles are small structures located in the skin that produce hair. Each hair follicle consists of several components, including:
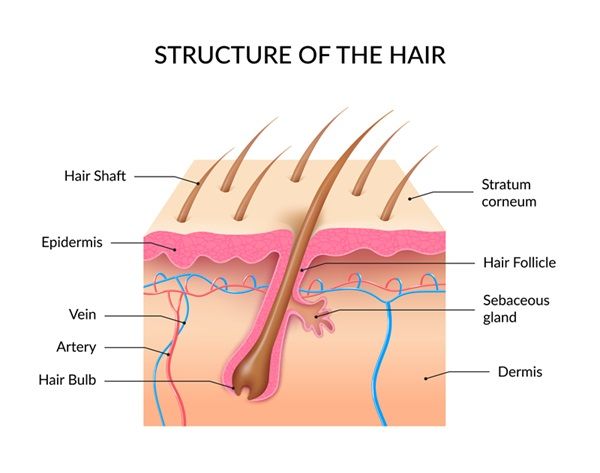
- Hair Shaft: This is the visible part of the hair that extends beyond the skin’s surface.
- Hair Bulb: The base of the hair follicle, where hair growth begins.
- Sebaceous Gland: These glands produce sebum, a natural oil that lubricates the hair and skin.
- Arrector Pili Muscle: A tiny muscle attached to the hair follicle that causes hair to stand on end when contracted (goosebumps).
Understanding the anatomy of hair follicles is crucial to comprehend how blockages can disrupt their normal functioning.
What are Blocked Hair Follicles?
Blocked hair follicles, also known as follicular occlusion disorders, occur when hair follicles become obstructed or clogged. This blockage can be caused by various factors, including dead skin cells, excess oil, dirt, and sometimes even bacteria. When a hair follicle is blocked, it can lead to various skin and hair problems, such as acne, boils, ingrown hairs, and even hair loss.
Blocked hair follicles can manifest in two primary forms:
- Comedones: These are non-inflammatory blockages, including whiteheads and blackheads, which result from the accumulation of oil, dead skin cells, and debris within the follicle.
- Folliculitis: This is an inflammatory condition characterized by red, swollen, and pus-filled bumps. Folliculitis can be caused by bacterial or fungal infections of the hair follicles.
Common Causes of Blocked Hair Follicles
Several factors can contribute to the development of blocked hair follicles. Understanding these causes is essential for both prevention and effective management. Some common causes include:
- Excess Oil Production: Overactive sebaceous glands can produce excessive amounts of sebum, leading to clogged hair follicles.
- Dead Skin Cells: The shedding of dead skin cells can accumulate in hair follicles, blocking them and leading to various skin conditions.
- Hair Products: The use of certain hair care products, such as heavy conditioners or pomades, can contribute to follicle blockages.
- Friction and Irritation: Clothing or tight headgear that rub against the skin can irritate hair follicles, leading to inflammation and blockages.
- Bacterial and Fungal Infections: Infections of the hair follicles can cause inflammation and blockages, leading to conditions like folliculitis.
- Ingrown Hairs: When hair grows back into the skin instead of emerging from the follicle, it can cause inflammation and blockage.
Recognizing Symptoms of Blocked Hair Follicles
The symptoms of blocked hair follicles can vary depending on the severity of the blockage and the specific condition. Here are some common signs to watch out for:
- Blackheads and Whiteheads: These are typically the earliest signs of blocked hair follicles. Blackheads are open comedones, while whiteheads are closed ones.
- Painful Bumps: Inflammatory conditions like folliculitis can lead to painful, red bumps filled with pus.
- Cysts and Nodules: Severe cases of blocked hair follicles may result in the formation of deep cysts or nodules beneath the skin.
- Itching and Discomfort: Blocked hair follicles can cause itching and discomfort in the affected area.
- Hair Loss: When the blockage affects the hair follicles on the scalp, it can lead to hair thinning or hair loss.
Conditions Associated with Blocked Hair Follicles
Blocked hair follicles can give rise to a range of skin and hair conditions. Let’s take a closer look at some of these conditions:
- Acne: Comedones and inflammatory acne can be triggered by blocked hair follicles. Acne is a common skin condition characterized by pimples, blackheads, and whiteheads.
- Folliculitis: This condition is marked by red, painful bumps caused by the inflammation of hair follicles, often due to bacterial or fungal infections.
- Hidradenitis Suppurativa: A chronic skin condition characterized by recurrent, painful abscesses and boils, usually affecting the armpits, groin, buttocks, and under the breasts.
- Ingrown Hairs: When hair grows back into the skin instead of outward, it can lead to ingrown hairs, which often become infected and inflamed.
- Cicatricial Alopecia: In some cases, chronic inflammation of hair follicles can lead to permanent hair loss, a condition known as cicatricial alopecia.
Prevention of Blocked Hair Follicles
Preventing blocked hair follicles is crucial for maintaining healthy skin and hair. Here are some effective strategies to prevent blockages:
- Proper Hygiene: Regular cleansing of the skin and scalp helps remove excess oil, dead skin cells, and dirt, reducing the risk of blockages.
- Gentle Exfoliation: Using mild exfoliants can help remove dead skin cells that can clog hair follicles. Be careful not to over-exfoliate, as this can irritate the skin.
- Avoid Heavy Hair Products: Use hair care products that are non-comedogenic and avoid heavy conditioners and pomades, which can contribute to blockages.
- Loose Clothing: Wear loose-fitting clothing to reduce friction and irritation on the skin, especially in areas prone to folliculitis.
- Proper Shaving Techniques: Shave in the direction of hair growth to minimize the risk of ingrown hairs.
- Keep Skin Dry: For individuals prone to excessive sweating, keeping the skin dry and using antiperspirants can help prevent blocked sweat glands.
Treating Blocked Hair Follicles
If you suspect you have blocked hair follicles or are already experiencing symptoms, there are various treatment options available, depending on the severity of the condition:
- Topical Treatments: Over-the-counter creams or ointments containing salicylic acid, benzoyl peroxide, or retinoids can help treat comedones and mild cases of folliculitis.
- Oral Medications: In more severe cases, a healthcare provider may prescribe oral antibiotics or medications to reduce inflammation and control infection.
- Warm Compresses: Applying warm compresses to the affected area can help reduce inflammation, relieve pain, and encourage the drainage of pus in conditions like folliculitis.
- Drainage: In the case of deep cysts or abscesses, a healthcare provider may need to drain the affected area to promote healing.
- Laser and Light Therapy: These treatments can be effective for chronic conditions like hidradenitis suppurativa.
- Hair Removal: In cases of recurring ingrown hairs, laser hair removal or electrolysis may be recommended to prevent future occurrences.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Managing contributing factors like stress and obesity may be necessary in cases of chronic conditions associated with blocked hair follicles.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While many cases of blocked hair follicles can be managed with home care and over-the-counter treatments, there are instances when medical attention is essential:
- Severe Pain: If you experience intense pain or discomfort, especially with large cysts or abscesses, consult a healthcare provider.
- Recurring or Chronic Symptoms: If you have persistent or recurrent symptoms despite home care, it’s important to seek medical advice.
- Signs of Infection: Redness, warmth, swelling, and pus are signs of infection and should be assessed by a healthcare provider.
- Hair Loss: If you notice significant hair thinning or hair loss, consult a dermatologist to address the underlying issue.
Blocked hair follicles can be a source of various skin and hair issues, but with the right knowledge and care, they can be managed effectively. By understanding the causes, symptoms, prevention methods, and treatment options, you can maintain healthier skin and hair. Remember that while mild cases can often be addressed at home, it’s crucial to seek medical attention for severe or recurring issues to prevent complications and ensure long-term skin and hair health.
