Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) | DocIndia.org
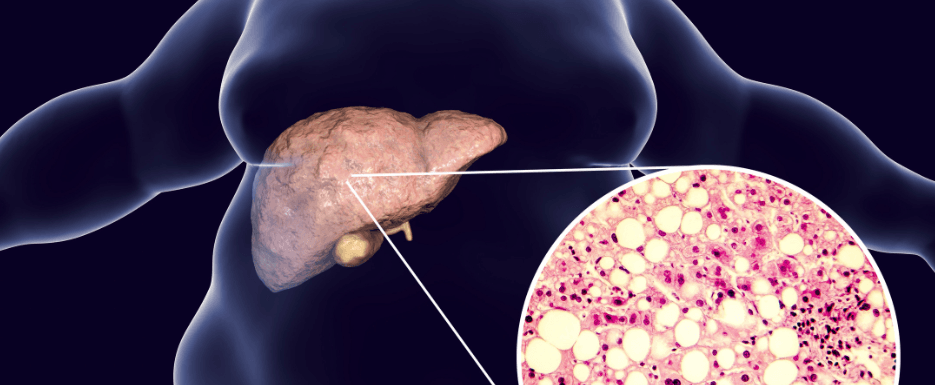
In recent times, many people are known to suffer from various types of liver problems, the intensity of which may vary from one person to another. Though one may think that in most cases, liver diseases develop due to the intake of alcohol, some conditions may occur due to other reasons as well. One of them can be non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, or NAFLD.
This article will help you to get a complete and detailed idea about the types of health conditions that may result in the occurrence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, what happens if you develop this disease, along with the possible symptoms, the diagnosis and treatment methods, and other related details.
What is the non-alcoholic fatty liver disease all about?
A non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is a kind of disease that affects the healthy functioning of the liver, and as the name suggests, it does not develop as a result of the consumption of alcohol as part of your daily lifestyle. This disease usually develops among those who have almost little or no amounts of alcohol.
Though its occurrence is not specific, there can be a common demography found for the non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. This disease is usually found to develop in the Middle Eastern and Western countries. The most probable reason behind such occurrences may be obesity and the deposition of fat in some of the major and most crucial digestive organs, like the liver. A condition known as steatosis occurs when around 5 to 10 percent of the liver’s weight is fat, and the doctor declares that the person has developed fatty liver disease.
The severity of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease may vary from conditions such as hepatic steatosis, also known as fatty liver, to a more severe form of liver damage known as nonalcoholic steatohepatitis or NASH.
What are the symptoms of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease?
The signs that indicate that you are developing non-alcoholic fatty liver disease may differ from one person to the other. In fact, in most cases, during the primary stage of development of this disease, it is truly difficult to identify any particular or significant symptom of the disease.
When a person develops non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, there are chances that the person would initially experience signs of excessive weakness and fatigue, pain or discomfort that develops in the upper right area of the belly, a condition of malaise or not feeling well, problems related to indigestion, and so on. But these symptoms are not enough for you to understand whether you have non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Still, certain common symptoms may develop as a result of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, which can indicate that you are gradually developing the disease inside your body, and the liver condition and functioning are slowly being affected. Some such types of symptoms may include the following:
• Itchiness of the skin.
• Pain and swelling of the legs.
• Yellowing of the skin and eyes, or frequent occurrence of jaundice.
• Abdominal swelling, usually known as ascites.
• Problems while breathing due to shortness of breath.
• Spider-like blood vessels just beneath the skin's surface.
• Enlarged spleen.
• Your palms turn red.
These symptoms may also occur if you are developing cirrhosis, scarring, or any type of severe damage to your liver. So, if you notice any of these symptoms, you should consult a health care professional at once.
How do doctors diagnose non-alcoholic fatty liver disease?
Doctors usually recommend various types of diagnostic procedures that are beneficial for the patient’s recovery. This is because the test results will help in determining the conditions of the non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, which will help the doctor to choose a treatment method accordingly, and this will help in better and faster recovery from the disease.
1. Liver Function Test:
There are certain common types of tests that doctors often recommend their patients undergo for diagnosing conditions like non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Function Test or LFT is one such type of test. A liver function test is, in fact, a very common diagnostic procedure for detecting fatty liver or similar types of liver problems by revealing any type of fatty accumulation in the liver, which results in the gradual damage of the organ, along with other types of problems in the liver, such as inflammation, scarring, and so on.
2. Liver Scan:
A scan of the liver can also show abnormalities in the functioning of the liver, which may indicate the occurrence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Doctors may also recommend CT scans, MRI scans, or even ultrasounds and similar types of imaging tests that can help in understanding the progress of the disease and will allow the doctors to choose a treatment procedure based on the results.
A scan of the liver will not only show an enlarged liver for better diagnosis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, but will also show signs of other causes of various types of liver problems.
3. Liver biopsy:
The biopsy of the liver is also a very common type of diagnostic procedure that is often recommended by healthcare professionals during the diagnosis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. This test can help reveal whether there is any type of cancerous growth in the liver and the extent of damage that has taken place, so that the doctor can help treat the condition accordingly. Doctors may recommend a small sample to be collected from the liver during biopsy for detecting further deterioration from non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
4. Various types of blood tests:
The most common types of diagnostic tests that doctors recommend their patients to go through, if they are suspected to develop non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, include blood tests. If you undergo blood tests for the diagnosis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, then you are most likely to check for the signs of fibrosis or scarring of the liver through the tests as recommended by your concerned health care expert. A common type of blood test that doctors often recommend for their patients for diagnosing liver diseases may include Enhanced Liver Fibrosis or ELF.
Treatment and prevention of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease:
Health care professionals may choose various types of methods that may be crucial for treating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. The treatment methods that are chosen will differ from one patient to another, depending on different types of factors such as the severity of the disease, the person’s age and health conditions, whether the patient has any underlying health issues, and so on. In most cases, doctors recommend medications to their patients for the treatment of these types of liver diseases. Alongside, the patient may be advised to follow a healthy lifestyle.
Some of the most common types of treatment options for curing non-alcoholic fatty liver disease may include the following:
1. Reducing your body weight:
It is important to get rid of body weight to reduce body fat, especially when you have non-alcoholic liver disease. This is because experts often claim that obesity can worsen these types of liver conditions.
2. Consume a healthy and balanced diet:
In case of fatty liver disease, it may be suggested that the patient consume a healthy and balanced diet that is free from junk and processed foods. That is to say, it is important to make sure that there is no further fat deposition in the liver as a result of the food that you consume.
3. Exercise daily:
Performing exercises can help reduce the chances of fat deposition in the liver. Moreover, exercising can also aid in the better functioning of the liver, which helps to enhance the digestive system.
You must also be in touch with your concerned gastroenterologist or hepatologist while you are in the treatment procedures for non-alcoholic liver disease.
Conclusion:
Non-alcoholic liver function disease is a common type of liver disease that may range from metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic disease or MASLD. This condition usually develops due to the accumulation of excess amounts of fats in the liver and not due to the intake of alcohol. The liver's functioning is affected, and the condition of the liver gets damaged as it swells up as a result of fat deposition.
There are certain symptoms of this disease that you must pay attention to. After diagnosis, it is important for you to consult an expert for treatment. If left untreated for a long time, this type of fatty-liver disease may lead to conditions such as liver scarring, known as cirrhosis, or even severe conditions like liver cancer.
