Male Sexual Organs and Pregnancy

Both a man and a woman equally participate in the process of childbirth. Both male and female reproductive organs are crucial and help in pregnancy after successful intercourse.
During intercourse, a man, on average ejaculates roughly 40 million to 150 million sperms, the male reproductive units that enter the ovary, the female reproductive organ, and thus get into the fallopian tubes of the female body. Once the sperms enter the fallopian tube, they start combining with the eggs out of which only one egg is fertilized.
The Male Reproductive System:
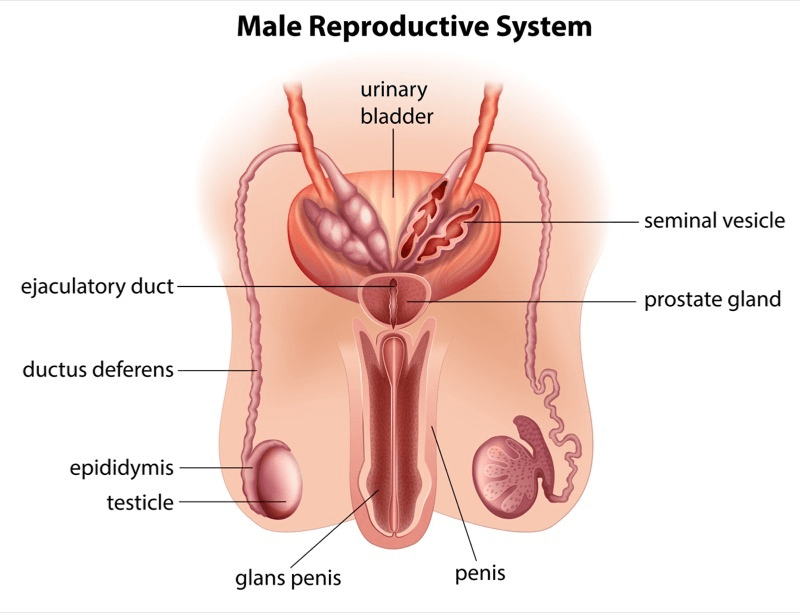
Apart from the female sex organs, the male reproductive system is also equally important to contribute to the pregnancy. The male reproductive system is present in the male body as an external organ system, connected to the outside of the body. The external organs are the penis, scrotum, and testicles. Though there are some internal organs, also known as ‘accessory organs’ in the male reproductive system, such as the vas deferens, prostate, and urethra, the external organs play the most significant roles. The organs in the male reproductive system are involved in sexual functions such as intercourse and thus in due course help in pregnancy and also helps in urination. The basic functions of the male reproductive system can be summed up as the following:
- The male reproductive system helps to manufacture sperms and helps in the effective movement of the sperms and fluid surrounding the sperm known as semen into the ovary.
- And helps to secrete and regulate the male sex or gonadotropic hormones.
The major portion of the male sex glands is situated in the external part of the abdominal cavity or pelvis. In men, the external reproductive organs are:
- Penis: The penis is a tube-like, muscular male reproductive organ that enhances intercourse as it contains blood during arousal. It is one of the primary organs that contribute to sexual reproduction in males and consists of three parts:
- The root: The root of the penis gets connected to the abdominal wall.
- The body or shaft: The body of the penis is the most important portion that is made up of loose and elastic skin takes the shape of a tube or cylinder and can be divided into three internal chambers within which there is a lining of erectile tissue and changes size during erection. This lining of tissues is made up of large spaces that fill during erection and arousal.
- The glans: This is the cone-shaped end of the penis. The glans, which or the head of the penis, is the cone-shaped apex of the penis that is covered with a loose layer of skin called the foreskin.
- Scrotum: The scrotum is a small triangular pouch-like sac that hangs at the end of the penis and consists of nerves and blood vessels that mainly holds the testicles or testes and helps in encasing the penis and protects it from any kind of harsh climatic condition which is necessary for controlling the sperm count. Moreover, the scrotum contains special muscles that help in the contraction and relaxation of the testicles.
- Testicles: Testicles are the two oval-shaped organs that are found within the testes, the primary male reproductive organs are known to contribute in male reproduction by manufacturing the male reproductive hormone known as testosterone, the primary male sex hormone, and producing the male reproductive units known as sperms. The testicles are again made of coiled tube-like masses that are known as seminiferous tubules that take an active part in the process of producing sperms, known as ‘spermatogenesis’.
- Epididymis: The epididymis is a long, coiled tube that is present on the backside of each testicle, and it helps to store sperm cells within the testes. This gland is also responsible for making the sperm cells mature for effective fertilization.
All men are born with external reproductive organs, but these are not functional from the time of their birth. The role of the gonads and reproductive organs and hormones come into play since the time of their adolescence. During puberty, the male body secretes a hormone known as testosterone that is produced from the male reproductive organ called the testes. The testosterone hormone is not only the male reproductive hormone but also helps in the breaking of voice, growth of beards, and mustache in the male body. The testes contain further smaller reproductive organs known as testicles that manufacture sperms that are ejaculated during fertilization along with a substance known as semen that is formed due to a fluid mixture coming from the prostate gland and the seminal vesicles. This mixture of fluids and sperms that are secreted from the male reproductive glands that come out along with the sperms during ejaculation of sexual intercourse and enters the female body in the process helps to provide nourishment to the female reproductive system.
Functions Of the Male Reproductive System in Pregnancy:
Essential chemicals known as hormones play the most vital roles in shaping the male reproductive system. The primary hormones that are responsible for the functioning of the male reproductive system are follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), and testosterone.
FSH and LH are known as ‘pituitary hormones’ that are mainly produced from the pituitary gland located within the brain. Follicle-stimulating hormone or FSH is primarily involved in the process of production of male reproductive units or sperm cells- a process known as spermatogenesis. LH or luteinizing hormone enhances the secretion of the male sex hormone testosterone that develops male characteristics such as breaking of voice, growing of muscles and beards during puberty and plays a role in sperm movement in sexual reproduction.
The internal organs in a male reproductive system:
The anatomy and the functions of the internal organs in a male reproductive system are as follows:
- Vas deferens: The vas deferens is a long, tubular muscular organ that moves from the epididymis to the pelvic cavity, to just behind the bladder and helps in the transportation of mature sperm cells in the urethra and prepares it for ejaculation.
- Ejaculatory ducts: These are formed by the fusion of the vas deferens and the seminal vesicles that travels into the urethra.
- Urethra: The urethra is an essential internal male sex organ that not only carries urine from the bladder and removes it out of the body but also contributes to ejaculation of sperms in sexual reproduction.
- Seminal vesicles: These vesicles are basically sac-like pouches that are attached to the vas deferens near the base of the bladder and are responsible for secreting a fluid that provides energy to the sperm cells which is derived from the sugar or fructose components in the fluid.
- Prostate gland: The prostate gland is an internal male organ that is placed below the urinary bladder in front of the rectum and produces a fluid that helps in effective ejaculation and for providing nourishment to the sperm cells. The prostate gland contributes additional fluid to the ejaculate. Prostate fluids also help to nourish the sperm.
- Bulbourethral glands: The bulbourethral glands also known as the Cowper’s glands are the internal glands of the male reproductive system that takes a pear-like shape and it is situated on the sides of the urethra, just below the prostate gland that helps in the secretion of a slimy, transparent fluid that flows into the urethra and this fluid plays a vital role in lubricating the urethra and to neutralize any acidity in the urethra and maintains the proper pH.
How Men Can Enhance Fertility?
Some men find it difficult to contribute to successful pregnancy after intercourse. Here are some ways that will effectively help men to boost their fertility:
- Reduce stress disorder and practice relaxation.
- Quit smoking, drinking alcohol, or the consumption of any other drugs.
- Have a healthy and balanced diet that consists of high amounts of minerals like zinc (especially foods like meat, whole grains, seafood, and eggs), selenium (seafood like fish, mushrooms, cereals, whole grains, and Brazil nuts), and vitamins like vitamin E.
- Control the number of sperms at an optimum and try to keep your testicles cool by avoiding long, hot baths or saunas.
- Cut down obesity.
Fertility gets reduced among Older Men: As age increases, fertility in men increases because with age, the sperm count, and effective sperm movement decrease. This further affects the sexual functions and thus interrupts intercourse which does not lead to a successful pregnancy. Though there is no particular age limit, late age sometimes affects fertility and reproduction in men.
