How to help a child with tongue tie?
WHAT IS TONGUE TIE? WHAT PARENTS NEED TO KNOW?
As parents, we often find ourselves navigating through a myriad of concerns and questions about our children's health and development. One such concern that may arise is tongue tie, a condition that affects infants and can impact their ability to breastfeed, eat, and even speak properly. In this article, we'll delve into what tongue tie is, how it affects infants, and what parents need to know if their child is diagnosed with this condition.
What is Tongue Tie?
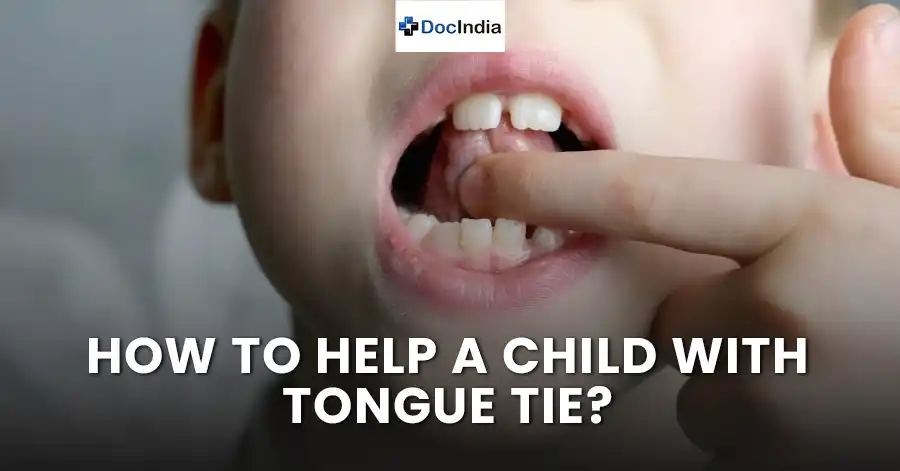
Tongue tie, medically known as ankyloglossia, is a condition present at birth that restricts the movement of the tongue due to an unusually short, thick, or tight band of tissue (lingual frenulum) that attaches the underside of the tongue to the floor of the mouth. This condition can vary in severity, with some cases causing minimal disruption, while others can significantly impair tongue movement.
Types of Tongue Tie:
Tongue tie can manifest in different degrees, depending on the extent to which the lingual frenulum restricts tongue movement. The severity of tongue tie is often classified into the following types:
- Anterior Tongue Tie: In this type, the lingual frenulum attaches close to the tip of the tongue, limiting its range of motion.
- Posterior Tongue Tie: Here, the attachment of the lingual frenulum is further back towards the base of the tongue, which may be harder to diagnose and can cause more significant functional issues.
Symptoms of Tongue Tie:
Identifying tongue tie in infants can be challenging, as not all cases present with obvious symptoms. However, some common signs that may indicate tongue tie include:
- Difficulty latching onto the breast during breastfeeding
- Poor weight gain or inadequate nutrition intake
- Clicking noises while nursing
- Nipple pain or damage for the breastfeeding parent
- Gassiness or colic-like symptoms in the infant
- Difficulty sticking out the tongue beyond the lower front teeth
- Speech delays or difficulty articulating certain sounds as the child grows older
Understanding the Frequency of Tongue Ties
Tongue ties, while not uncommon, vary in prevalence due to differences in defining and diagnosing the condition. Exact statistics are challenging to determine, but it is estimated that around 8% of infants under the age of one may exhibit at least a mild form of tongue tie. This paragraph aims to provide parents with an understanding of the prevalence of tongue ties among infants, highlighting that it is a relatively common condition.
Assessing the Impact of Tongue Ties
It's crucial to recognize that tongue ties are not inherently problematic for everyone who has them. Many babies, children, and even adults have tongue ties that do not cause any difficulties whatsoever. However, there are instances where tongue ties can lead to challenges, primarily in two areas: breastfeeding and speech. This paragraph clarifies that while some infants may experience difficulty latching onto the mother's nipple during breastfeeding due to a tongue tie, not all babies with tongue ties encounter this issue. Additionally, tongue ties are not responsible for gassiness or fussiness in breastfed babies who are gaining weight adequately, nor do they typically affect bottle feeding. The paragraph also highlights that some children with tongue ties may struggle to pronounce certain sounds, but tongue ties do not cause speech delays. Overall, it emphasizes that the impact of tongue ties varies among individuals and is not universally problematic.
Seeking Professional Guidance for Tongue-Tie Concerns
- If you suspect that your baby or child has a tongue tie, it's essential to seek guidance from healthcare professionals. This importance of talking to your doctor if you believe that your newborn is having difficulty latching onto the breast due to a tongue tie. It advises parents that there could be various reasons why a baby struggles with breastfeeding, and a thorough evaluation by a doctor is necessary to understand the situation accurately.
- Furthermore, it is suggested to schedule a visit with a lactation specialist to receive support with breastfeeding. It acknowledges that many babies with a tongue tie can successfully nurse with the right techniques and assistance. Consulting with a lactation specialist can provide parents with valuable guidance and strategies to improve breastfeeding outcomes.
- Additionally, if parents suspect that a tongue tie may be affecting their child's speech, the paragraph encourages them to discuss their concerns with a doctor. However, it also stresses the importance of not immediately attributing speech difficulties to a tongue tie without proper evaluation. Seeking an assessment from a speech therapist can help determine the underlying cause of speech issues and guide appropriate intervention strategies.
Managing Tongue-Tie: Treatment Strategies
- When necessary, doctors can address tongue-tie through a procedure known as frenotomy. This intervention involves releasing the tight frenulum, either by snipping it with scissors or using a laser. It's important for parents to understand the available treatment options for tongue-tie, which this section outlines.
- Moreover, it's essential to recognize that intervention should only occur if the tongue-tie is causing significant problems. The potential for complications, such as bleeding, infection, or feeding difficulties, underscores the need for careful consideration before proceeding with frenotomy. It's not advisable to intervene solely as a preventive measure for future issues.
- Additionally, while frenotomy may alleviate breastfeeding difficulties for some infants, it's not a guaranteed solution. Studies suggest varying outcomes for both babies and mothers following the procedure. Therefore, collaboration with a lactation expert is crucial before considering frenotomy, as breastfeeding challenges may have multifaceted causes.
- In cases where breastfeeding problems persist despite support from a lactation expert, frenotomy may be a viable option, especially if there are concerns about inadequate weight gain. Early intervention is emphasized, and parents are encouraged to seek the procedure from a healthcare professional with expertise in performing frenotomies. This section aims to provide parents with comprehensive information about managing tongue-tie, emphasizing the importance of informed decision-making and collaboration with healthcare professionals.
Why is Tongue Tie a Concern?
- Tongue tie can pose several challenges for infants and their families. One of the most significant concerns is its impact on breastfeeding. Babies with tongue tie may struggle to latch effectively, leading to insufficient milk transfer and potential complications such as low milk supply for the breastfeeding parent and inadequate nutrition for the infant. This can result in weight loss or failure to thrive if left unaddressed.
- Beyond infancy, untreated tongue tie can also affect speech development. The limited mobility of the tongue may hinder the child's ability to form certain sounds, leading to speech impediments or delays in language acquisition. Additionally, tongue tie can contribute to oral hygiene issues, as restricted tongue movement may make it difficult to clean the mouth properly, potentially increasing the risk of dental problems such as tooth decay and gum disease.
Diagnosis and Treatment:
- Diagnosing tongue tie typically involves a physical examination by a healthcare provider, such as a pediatrician, lactation consultant, or pediatric dentist. During the assessment, the provider will evaluate the appearance and mobility of the tongue, as well as observe the infant's ability to breastfeed or suck from a bottle.
- If tongue tie is confirmed and causing significant issues, treatment may be recommended to release the tight frenulum. This procedure, known as a frenotomy or frenectomy, involves cutting or lasering the frenulum to allow for greater tongue mobility. In some cases, a multidisciplinary approach involving lactation support, speech therapy, and oral motor exercises may also be recommended to address any associated feeding or speech difficulties.
What Parents Need to Know:
For parents whose infants are diagnosed with tongue tie, it's essential to gather as much information as possible to make informed decisions about their child's care. Here are some key points to consider:
- Seeking Support: Don't hesitate to reach out to healthcare professionals for assistance if you suspect your child has tongue tie or are experiencing difficulties with breastfeeding or feeding in general. Lactation consultants, pediatricians, and pediatric dentists can offer guidance and support tailored to your child's needs.
- Exploring Treatment Options: Discuss the available treatment options with your healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate course of action for your child. While frenotomy is a common and relatively simple procedure, it's essential to weigh the potential benefits against any risks or considerations specific to your child's situation.
- Post-treatment Care: After undergoing a frenotomy, your child may require some postoperative care, such as wound management and oral exercises to promote tongue mobility. Follow your healthcare provider's instructions carefully and attend any follow-up appointments to monitor your child's progress.
- Monitoring Development: Keep an eye on your child's feeding patterns, weight gain, and overall development following treatment for tongue tie. While many infants experience improvement in breastfeeding and feeding difficulties after a frenotomy, some may require additional support or interventions to address lingering issues.
- Advocating for Your Child: As a parent, you are your child's best advocate. Trust your instincts and speak up if you have concerns about your child's health or development. Be proactive in seeking out resources and support networks to help you navigate the challenges associated with tongue tie and its treatment.
In conclusion, tongue tie is a common condition that can impact infants' breastfeeding, feeding, and speech development. While it can pose challenges for families, timely diagnosis and appropriate intervention can help alleviate symptoms and promote optimal oral function and development. By staying informed, seeking support, and advocating for their child's needs, parents can play a crucial role in managing tongue tie and ensuring their child's overall well-being.
