Digestive System (Anatomy): Process Parts and Functions
"Mustn’t regret what you eat, so eat a proper healthy meal to help your body heal.”
The human body is an amazing machine and is also the most complex organism on this planet. It consists of different cells, tissues, organs, and systems. 11 organ systems in the human body have their own functions to perform for human beings’ healthy functioning and survival. Now, the most common thing is, we eat food twice or thrice a day to obtain energy and perform our daily tasks. Have you ever wondered how and where does the food we consume goes and how we get energy from it? Here comes the exceptionally powerful and well-organized system of the human body, which is the DIGESTIVE SYSTEM.
Basically, Digestive System is the system that contributes to the digestion of food. When we eat food such as vegetables, fruits, meat, and bread, they are not in such a form that our body can directly extract nutrients from them. In this case, it becomes important that the food must be broken into smaller molecules of nutrients before it is being absorbed into the blood and carried to cells throughout the body. Thus, Digestion is the process in which food that we intake is broken down into its smallest parts so that it can be used to build and nourish cells and provide energy to the body. The digestive system is the system that consists of several organs that carry forward the digestion of food. It starts from our mouth and ends at the anus. All animals have a digestive system though it differs in shape and size. For instance, humans have only one stomach, but the cow has four stomachs (NCERT, Class7: chapter2, Nutrition in Animals). Thus, it depends upon the function and individual’s requirements. Convincingly, the human digestive system is a complex series of organs and glands that processes food and convert ingested food into smaller units to assimilate the organism.
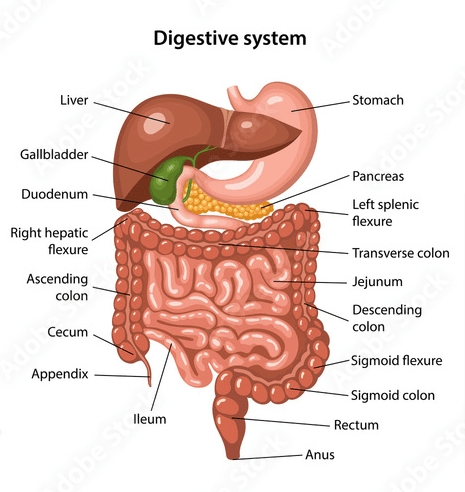
ORGANS OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEM: The human digestive system comprises of different organs through which food travels as;
- Mouth: It is generally known as the oral or buccal cavity. Food and saliva are received by the mouth. Digestion starts in the mouth, where the chewing of the food takes place by the teeth and it is moistened with saliva (containing enzyme which help in breakdown of carbohydrate into sugar), making it easy to swallow.
- Esophagus: It connects pharynx which is the opening of the oral and vassal cavities with the stomach. By its contractions the swallowed food is taken down into stomach.
- Stomach: It is a J-shaped, muscular, hollow, and dilated part of digestive system. It is situated between esophagus and the small intestine. It secretes protein- digesting enzymes called proteases and strong acids such as HCl that helps in the digestion of food.
- Small Intestine: It is located in between the stomach and the large intestine. It consists of three parts namely, Duodenum, Jejunum, and Ileum.
- Large Intestine: It is also known as colon, it is made up of the cecum, the ascending colon, the transverse colon, the descending colon, and the sigmoid colon, which connects to the rectum.
- Rectum: It is a straight 8-inch chamber that connects the colon to the anus.
- Anus: The anus is the last part of the digestive system. It is 2-inch-long canal from where the waste is excreted.
WORKING IN DIGESTIVE SYSTEM: Knowing how the human digestive system works is an important and a lot more interesting part. There are certain steps taken by the food we intake before exiting food from our body. Through the mouth, the intake of food takes place, where saliva helps in the breakdown so that it is easily absorbed. After that, the food reaches the stomach through Esophagus. Then the food is stored in the stomach and further is broken down by acid and powerful enzymes present there such as HCl. From there, the food moves into the small intestine where food is broken down into smaller particles by the enzymes released from the pancreas and the bile juice from the liver. Most nutrients are absorbed here. Whatever is left here is transferred to the large intestine or colon. The large intestine is responsible for the processing of the waste. On average, it takes approximately 36 hours for the waste to get through the large intestine and rectum and exit through the anus.
How is the Digestive System Controlled?
1. Hormone Regulators: The hormones that control the functions of the human digestive system are produced by cells in the mucosa of the stomach and small intestine. The hormones that control the digestion process are gastrin, secretin, and cholecystokinin (CCK).
- Gastrin: Its presence in stomach causes the production of an acid which helps in dissolving and digesting food.
- Secretin: It indicate pancreas to send out a digestive juice rich in bicarbonate that helps to neutralizes the acidic stomach contexts as they enter the small intestine. It also stimulates the stomach and liver to produce pepsin which digests protein and bile juice respectively.
- Cholecystokinin (CCK): It causes pancreas to produce pancreatic juice and promotes normal cell growth of pancreas.
Other hormones in the human digestive system to regulate appetite are Ghrelin and Peptide YY. Both of these hormones work on the brain to help regulate the intake of food for energy production.
2. Nerves: Two types of nerves help to control the action of the digestive system.
- Extrinsic: It comes to the digestive organ from the brain or the signal cord.
- Intrinsic: It makes up a very dense network embedded in the walls of Esophagus, stomach, small intestine and large intestine or colon.
Together, nerves and hormones, the blood, and the organs of the digestive system conduct the intrinsic task of digestion and absorption of nutrients from the food we consume every day.
Disease: A little digestive distress will mostly occur in everyone’s life who has a bit of poor indigestion or due to any other problem. Be it is a meal that doesn’t agree with the body and its function or a lingering gastrointestinal ailment requiring lifestyle changes and treatment, digestive problems are extremely common. Some of the digestive diseases and conditions are acute which lasts for a short time only but if not taken proper care they can be converted into chronic or long-lasting.
Some of the common problems in the Digestive system are:
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): It is a common disease which occurs in the digestive system. Its main symptom is abdominal pain, which occurs before or after bowel movements. In this case people may also experience diarrhea, constipation, or both. It can be reduced by reducing stress, making dietary changes etc.
- Gallstones: Gallbladder is a small sac that stores the bile juice which is used for digestion process. In the gallbladder small stones are formed known as gallstones. One may not know about the presence of the stones until and unless the gallstones form in front of the opening of the gallbladder. In this case the person may feel persistent pain below the ribs, high temperature, jaundice, sweating etc. It can be cured by the removal of gallstones through medicines or surgery.
- Diverticulitis: It is disease that results in the inflammation of pouches lining of the small intestine. In this case the person may feel nausea, pain the lower abdomen, cramps, constipation, fever etc. It can be cured through antibiotics or dietary change and if the condition is severe one might need to go under the surgery.
- Gastroenteritis: It is an infection in the intestine caused by bacteria or viruses that causes vomiting and diarrhea. It can be cured by changing the diet and drinking plenty of water along with the intake of antibiotics.
- Ulcers: It is the hole in the mucous membrane lining of the stomach or duodenum. In this case the person may face burning pain in between of upper and middle stomach which is temporary if antacid is taken, vomiting, nausea etc. It can be cured by using antibiotics, by drinking plenty of liquid and taking measure while eating the unnecessary food.
Thus, to avoid diseases or disorders of the digestive system, a change in diet and lifestyle can positively impact gut health. Here are few ways through which digestion can be improved.
- Eat healthy food.
- Get plenty of fiber.
- Add healthy fats to your diet.
- Stay hydrated.
- Eat on time.
- Chew food very properly.
- Exercise regularly.
- Drink warm water in the morning.
- Eat according to hunger.
- Quit bad habits such as smoking, alcohol, late night eating
Try to implement these and you are done!
Since the human digestive system starts the moment food touches the lips and is ingested through various organs to accomplish the functioning of this machinery. During this time various processes take place mechanical and chemical helping in digestion and providing energy to the body. So, it is important to take care of this delicate life processing machine to work properly, to maintain a healthy digestion system with the intake of healthy foods, and to adopt sensible eating habits which will relieve you from major disruptions to your life.
